|
Cisco Collaboration Flex Plan is available in the following license models:
The price changes based on the Flex version that is sold. Currently Cisco is selling Flex 3.0.
1 Comment
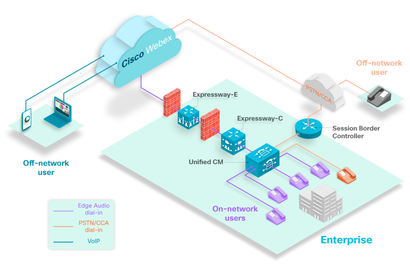
Webex offers a few different Webex Edge options. They can be confusing. I will try to outline what they are and what do they do: 1. Webex Edge AudioWebex Edge is a great cost saving feature for customers who utilize Webex Meetings and CUCM... This allows Webex Meetings to route PSTN calls through the internet and leverage on-premise CUCM for Webex Meetings Outbound/Call-Back feature - saving $$ on the Webex PSTN costs.. Here is a webex.com article on Webex Edge Audio. 2. Webex Edge ConnectWebex Edge Connect allows a customer to have a private point-to-point link between their network and Cisco Webex (Meetings and Calling) Cloud. This allows to by-pass public internet - thus guaranteeing bandwidth and quality of service (QoS). Here is a webex.com article on Webex Edge Audio. 3. Webex Edge Video MeshWebex Edge Video Mesh allows local (on-prem) media processing for cloud based media services thus improving the customer experience for on-prem users.
It is a software which is installed on-prem which is cloud managed by the Webex Control Hub. Here is a cisco.com article covering all of Webex Edge products. Misc
Webex Meetings
CCaaS - Webex Contact Center
CPaaS - Webex Connect
Agnostic Meetings
Developer Solutions |
AuthorSaad is a Senior Collaboration Engineer. He is CCIE x 3 (Collaboration, R&S and Data Center) Categories
All
Archives
May 2022
|











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
